Erreur de format d'e-mail
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd

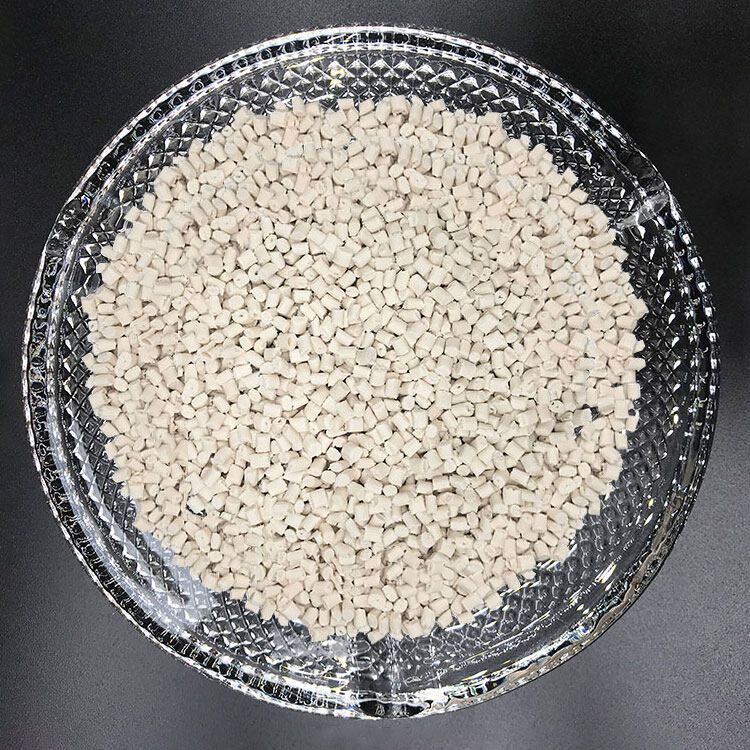
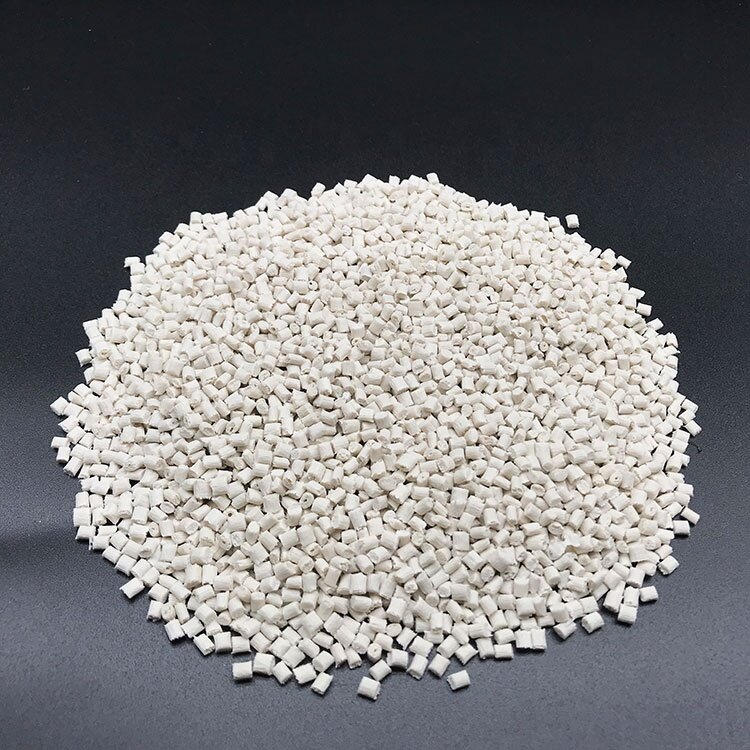
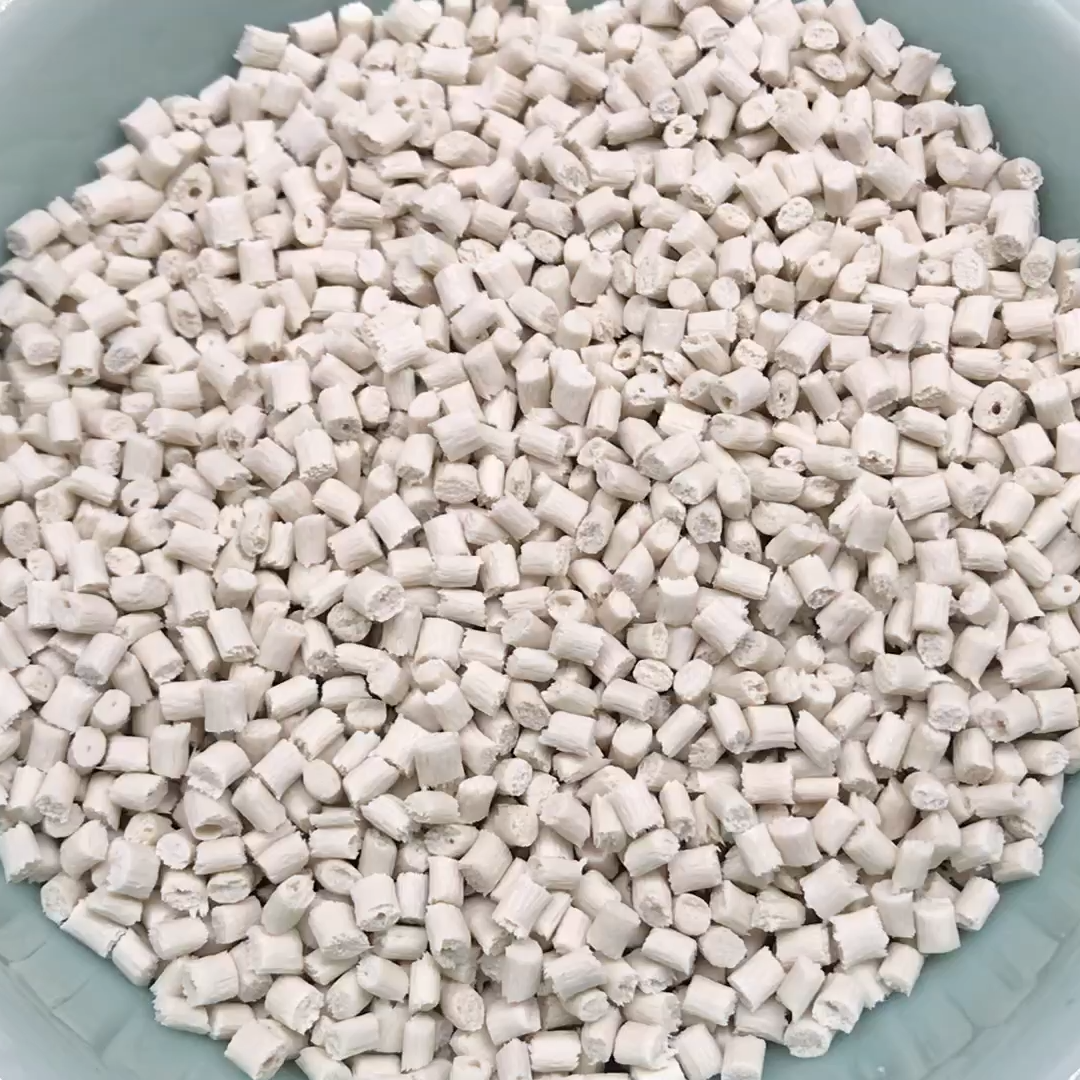
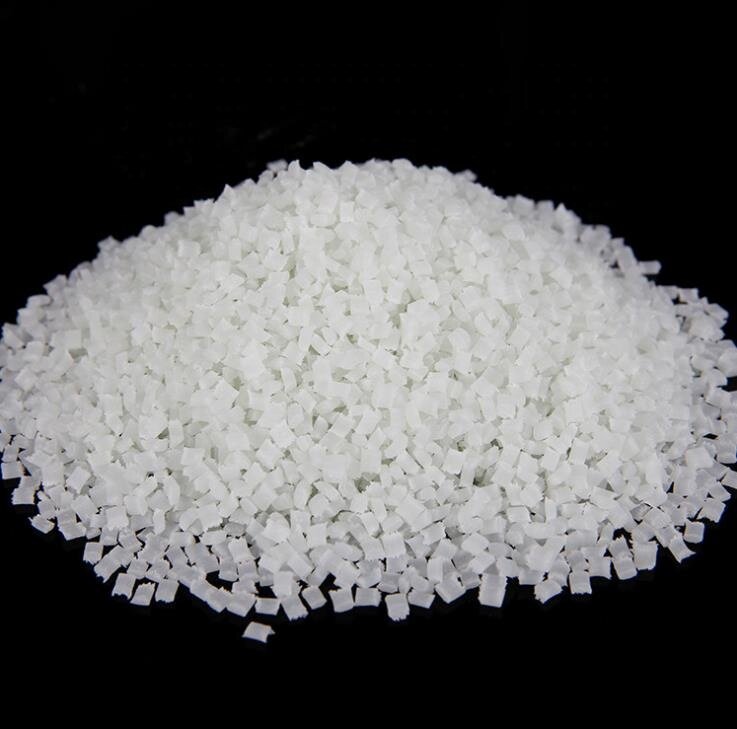
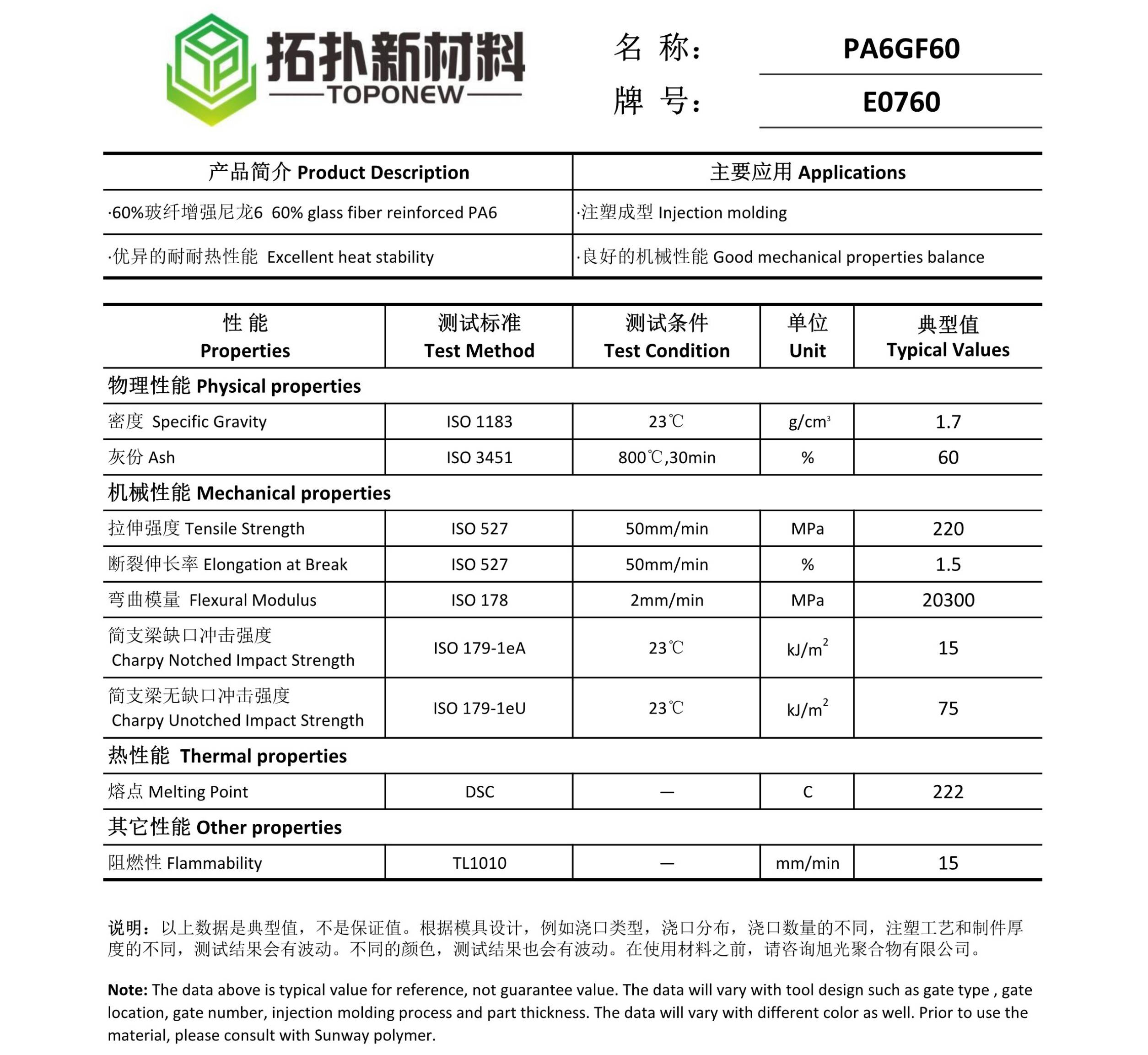
PA6 GF60 E0760
Glass Filled: 60%
(Custom materials available according to your Technical Data Sheet)
- Les détails du produit
-
Download

Customizable Materials Available:
- Color (Customization of plastic pellet color according to your requirements.)
- Flame retardant grade (Let us know which flame retardant level you need: 0.8mm-3.0mm HB, V0, V1, V2, 5VA, 5VB)
- Glass fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- Carbon fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- UV resistance property (Tell us the application scenarios or UV resistance level of the materials )
- Other materials can also be customized ( Just need to provide your Technical Data Sheet. )
Technical Data Sheet of PA6 GF60 E0760
The challenges in producing PA6 GF60 resin plastic pellets:
(PA6 plastic pellets with 60% glass fiber)
-
Dispersion: Achieving uniform dispersion of glass fibers in the plastic matrix can be challenging. Poor dispersion can lead to fiber agglomerates or uneven strength distribution in the final product. To address this issue, appropriate blending processes and additives should be used to ensure thorough dispersion of the glass fibers.
-
Mechanical properties: While the addition of glass fibers can significantly enhance the strength and stiffness of PA6, there can be challenges at higher glass fiber loadings. Excessive glass fiber content can result in increased brittleness or diminished reinforcing effects. Robust process development and formulation adjustments are necessary to meet strength requirements without sacrificing material toughness.
-
Cost considerations: Additionally, processing plastic pellets with glass fibers may require higher temperatures, pressures, and more wear-resistant mold materials, which can increase production costs. Consideration of both performance enhancement and cost factors is crucial before choosing to use PA6 GF60.
1.Polyamide 6 vs 66 (What is difference between nylon 6 and nylon 66?)
Nylon 6 and nylon 66 are both members of the polyamide family, widely known for their exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. While they share similarities, there are key distinctions between these two materials.
Nylon 6, also referred to as polyamide 6, is a type of polymer that offers excellent mechanical properties. It possesses high tensile strength, good impact resistance, and impressive toughness. This makes nylon 6 a suitable choice for various applications, including automotive parts, consumer goods, textiles, and industrial components.
On the other hand, nylon 66, or polyamide 6,6, is another type of polyamide known for its outstanding heat resistance and dimensional stability. It is formed by the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. Nylon 66 exhibits enhanced strength, rigidity, and resistance to elevated temperatures compared to nylon 6. Due to its excellent performance under heat, nylon 66 is commonly used in applications such as electrical connectors, mechanical parts, and automotive components.
2.Uses of Nylon 6 6 polymer
The uses of nylon 6,6 polymer are diverse and widespread. Its superior mechanical properties and resistance to heat and chemicals make it suitable for high-performance applications. The automotive industry often utilizes nylon 6,6 for fuel lines, cooling system components, and under-the-hood parts. It is also employed in electrical and electronic applications like connectors, switches, and insulators. In addition, nylon 6,6 is commonly found in consumer goods like sporting equipment, textiles, and packaging materials.
The significance of polyamide 6 vs. 66 nylon lies in their distinctive properties and applications. While nylon 6 exhibits excellent mechanical properties and is well-suited for various general-purpose applications, nylon 66 shines in demanding environments that require high heat resistance, dimensional stability, and enhanced strength.



Download
-
TOPONEW PA6GF60 Datesheet.pdf
Download TOPONEW PA6GF60 Datesheet.pdf









